Key points:
-
Researchers exploited modern electronics to develop a new, less painful and noninvasive way to estimate blood glucose levels.
-
Using an NIR sensor from a smartwatch, researchers linked metabolic index with blood glucose levels for the first time.
-
Clinical tests on diabetic individuals are pending to confirm the applicability of the metabolic index in a real-world context.
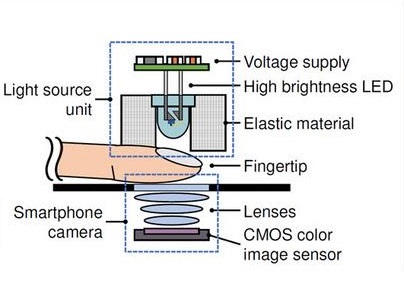
Blood glucose measurements (BGL) measurements typically involve drawing blood through a finger prick, but researchers want to leverage modern electronics to develop less painful and noninvasive alternatives. In a new study, published in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, a research team turns to near-infrared light (NIR) measurements to estimate BGL.
The team began by extracting oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) and deoxyhemoglobin (Hb) signals from NIR measurements. By analyzing this data, they determined that the phase delay between the low-frequency and oscillating components of HbO2 and Hb signals are closely linked to the degree of oxygen consumption during each cardiac cycle—an important metabolism indicator.
To test their newfound metabolic index, researchers placed an NIR sensor from a smartwatch over the finger of healthy participants at rest. The participants then consumed different sugary and sugar-free beverages, allowing the team to measure blood glucose changes. Excitingly, the changes in metabolic index matched variations in blood glucose as measured by a commercial continuous glucose monitor.
While the results confirm that the phase delay between HbO2 and Hb is correlated with BGL, the team needs to confirm the applicability of the metabolic index in a real-world context. These clinical tests would bring a practical, noninvasive way for people with diabetes to control their BGL.
“The proposed method can in principle be implemented in existing smart devices with a pulse oximetry function,” said Tomoya Nakazawa of Hamamatsu Photonics. “It is inexpensive, battery-saving, and simple compared with other noninvasive blood glucose monitoring techniques. Thus, our approach could be a powerful tool towards portable and accessible BGL monitoring devices in the future.”
TrendForce 2024 Infrared Sensing Application Market and Branding Strategies
Release: 01 January 2024
Format: PDF
Language: Traditional Chinese / English
Page: 172
|
If you would like to know more details , please contact:
|





 CN
TW
EN
CN
TW
EN






