 2016-11-04
2016-11-04
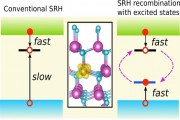
Using cutting-edge first-principles calculations, researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB) have demonstrated the mechanism by which transition metal impurities - iron in particular - can act as nonradiative recombination centers in nitride semiconductors. The work highlights that such impurities can have a detrimental impact on the efficiency of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) based on gallium nitride or indium gallium nitride.
Continue reading →
 2016-11-04
2016-11-04