The infrared Oslon black SFH 4725S is a secret agent in more ways than one. Not only does its light have a wavelength of 940 nanometers, making it virtually invisible to the human eye, but its black package reflects almost no ambient light whatsoever. Together with its high optical output of almost one watt, this infrared LED from Osram Opto Semiconductors is the ideal light source for covert surveillance.
Concealed security systems – such as those installed in banks, on machinery and at border controls – need to be designed so they are unobtrusive. This is a major challenge for infrared illumination in such applications because the 850 nanometer (nm) LEDs that are most often used here appear as weak dots of red light especially in dark environments. The solution is to switch to a wavelength of 940 nm, which the human eye is 130 times less likely to notice. Camera sensors however can easily detect this invisible radiation.
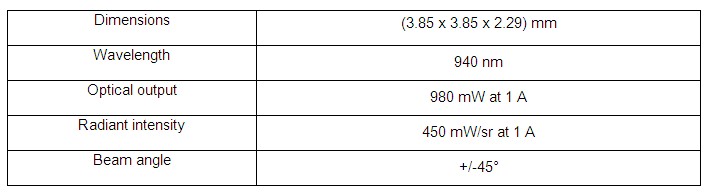
The Oslon black SFH 4725S from Osram Opto Semiconductors is the ideal component for such applications. This compact infrared LED provides 940 nm light with the high optical output of 980 milliwatts from an operating current of 1 amp. Behind this high performance lies the Nanostack technology in which Osram has succeeded in providing two emission centers in one chip, almost doubling the light output. The SFH 4725S achieves a radiant intensity of 450 mW/sr at an emission angle of 90 degrees and therefore provides excellent illumination over the area being monitored. Radiant intensity (measured in milliwatts per steradiant) indicates the light output within a solid angle segment and therefore defines the intensity of the light beam.
The black package ensures that the component is completely concealed behind the camera lens. “The 940 nm SFH 4725S is a further addition to our Oslon black series for the security sector, which already includes 850 nm versions with standard and Nanostack chips,” said Dr. Jörg Heerlein, Head of Product Marketing for industrial infrared components.
In the compact class the Oslon is currently one of the most powerful versions for both visible and infrared illumination. Measuring only 3.85 x 3.85 x 2.29 mm, the infrared Oslon components are among the smallest IREDs with around 1 W optical power, . “Users with experience in constructing visible lighting units can transfer their know-how and their processes directly to the infrared Oslon,” added Dr. Heerlein. The market is also full of lenses that designers can use to shape the beam from the IRED to meet their specific requirements.
Technical data for IR Oslon black SFH 4725S: