 2015-08-03
2015-08-03
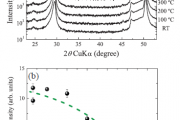
Ferroelectric materials have applications in next-generation electronics devices from optoelectronic modulators and random access memory to piezoelectric transducers and tunnel junctions. Now researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology report insights into the properties of epitaxial hafnium-oxide-based (HfO2-based) thin films, confirming a stable ferroelectric phase up to 450 °C. As they point out, “This temperature is sufficiently high for HfO2-based ferroelectric materials to be used in stable device operation and processing as this temperature is comparable to those of other conventional ferroelectric materials.”
Continue reading →
 2015-08-03
2015-08-03